Solar air conditioning systems, also known as solar-powered air conditioners, utilize solar energy to power the cooling. These systems work in a similar way to traditional air conditioners but with the added of using renewable energy sources.
Solar panel voltage:
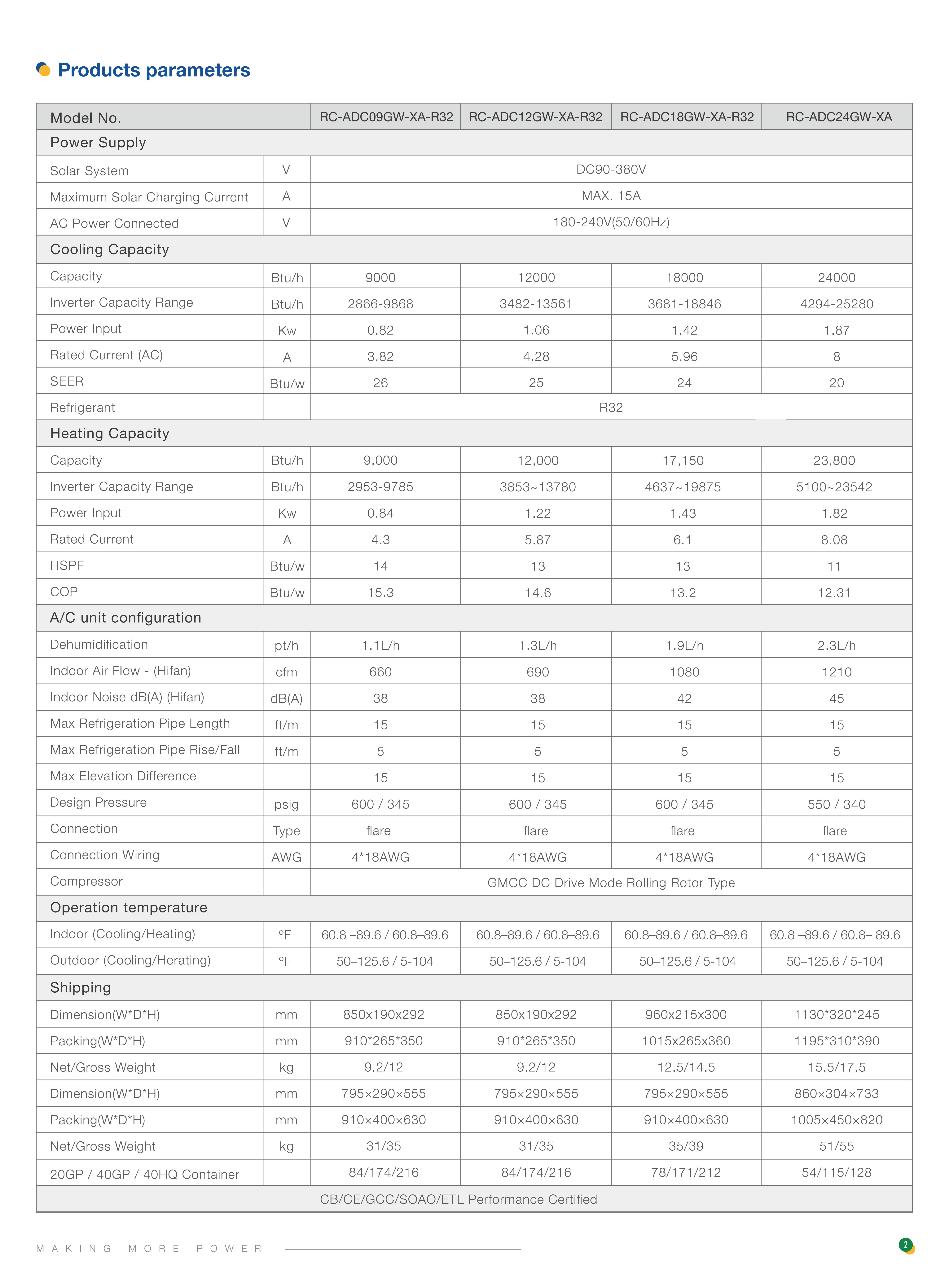
DC90-380VMaximum Solar Charging Current:
15AAC Power Connected:
180-240V(50/60Hz)Refrigerant:
R32Compressor:
GMCC DC Drive Mode Rolling Rotor TypeConnection:
Flare
A solar air conditioning system, also known as a solar-powered air conditioner or solar cooling system, uses solar energy to provide cooling for a building or space. Traditional air conditioners use electricity from the grid, whereas solar air conditioning systems utilize energy from the sun to operate.
Here's how a solar air conditioning system typically works:
Solar Panels: Photovoltaic (PV) solar panels are installed the roof or in a location to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. These solar panels consist of multiple solar cells that generate direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
Inverter: The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is then sent to an inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the type of electricity used in most homes and buildings.
Compressor and Condenser: The AC electricity powers the compressor and condenser unit of the air conditioning system. The compressor pressurizes and circulates a refrigerant fluid, typically a gas, through the system.
Evaporator and Expansion Valve: The refrigerant fluid is pumped to the evaporator coil inside the building or space that requires cooling. As the warm air from the space passes over the evaporator coil, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air, cooling it in the process.
Heat Exchange: The heated refrigerant gas then flows to the condenser coil located outside the building, where it releases the heat absorbed from the indoor air to the outside environment. This process cools down the refrigerant, and it returns to a liquid state.
Circulation and Control: The cooled liquid refrigerant is pumped back to the evaporator coil to repeat the cycle and continue cooling the indoor air. Various sensors, controls, and thermostats are used to monitor and regulate the temperature and operation of the system.

Advantages of solar air conditioning systems include:
Energy Savings: By utilizing solar power, these systems reduce or eliminate the need for electricity from the grid, resulting in lower energy bills.
Environmental Benefits: Solar air conditioning systems reduce reliance on fossil fuels and help minimize greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner and greener environment.
Energy Independence: Solar energy is a renewable resource, allowing users to generate their own electricity and reduce dependency on external energy sources.
Long-Term Cost Savings: Although the initial installation cost may be higher compared to conventional air conditioning systems, the long-term savings on electricity bills can make solar air conditioning systems a cost-effective choice.
Reliability: Solar energy is abundant in many regions, making it a reliable and consistent power source. Additionally, these systems often include backup batteries or connections to the grid, ensuring uninterrupted power supply even during periods of low sunlight.
It's important to note that the exact design and efficiency of solar air conditioning systems can vary. Consulting with a professional solar installer or HVAC specialist would provide more detailed and tailored information based on specific needs and location.
A solar air conditioning system uses solar energy to power the cooling process, reducing the reliance on traditional electricity. Here's a general overview of how it works:
Solar Panels: Photovoltaic (PV) solar panels are installed the roof or in an with good sun exposure. These panels convert sunlight into DC electricity.
Inverter: The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is sent to an inverter, which converts it into AC electricity suitable for powering the air conditioning system.
Air Conditioning Unit: The AC electricity is supplied to the air conditioning unit. The unit consists of a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. The process that follows is similar to a conventional air conditioner.
Cooling Process: The compressor in the air conditioning unit pressurizes the refrigerant gas, raising its temperature. This hot gas then flows into the condenser, where heat is released into the outdoor air. As a result, the refrigerant becomes a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
Expansion Valve: The high-pressure gas flows through the expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature, transforming it into a low-pressure, low-temperature gas.
Evaporator: The low-pressure gas enters the evaporator, where it absorbs heat from the indoor air. As the heat is absorbed, the refrigerant evaporates into a gas form.
Cooling and Dehumidification: The cooling effect created by the evaporation of the refrigerant removes heat from the indoor air. At the same time, the evaporator also helps remove excess moisture, providing dehumidification.
Air Distribution: The cooled and dehumidified air is blown into the indoor space using a fan or blower, circulating the cool air and improving comfort.
FAQs:
Q1: Do you support OEM/ODM?
A:Definitely, OEM&ODM service is supported with a certain quantity,including customize logo,package and label;
Q2: What's the production time?
A: The production time is normally 15 working days. but we will always prepare some stocks for popular models.
Q3: Can you provide DDP service?
A:Yes, if you are a personal customer and don't want to deal with the customs, we can provide DDP service to your address.
Q4: What about the warranty and how to claim?
A: Warranty period are 5 years since you receive the product, our professional after-sales team will deal with all warranty issues.