An EV charger, short for Electric Vehicle charger, is a device used to supply electric power to recharge the batteries of electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). EV chargers come in various types and configurations, each offering different charging speeds and compatibility with different vehicles.
Standard:
SAE Standard / IEC StandardConnector type:
Type 1 / Type 2Connector Mechanical Operating Life:
≥10000 times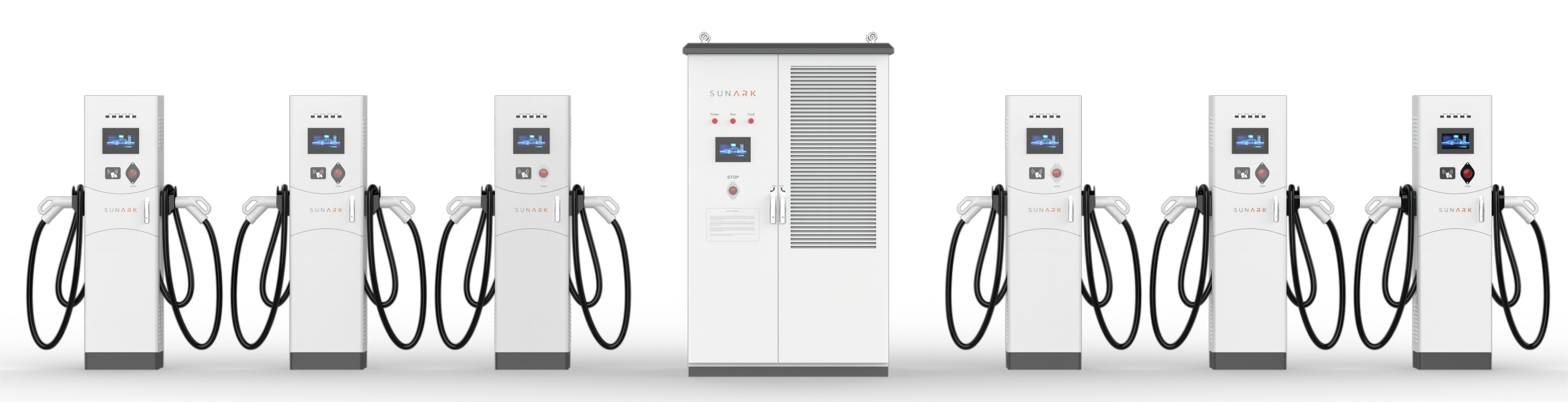
As of my last update in January 2022, the trend of EV chargers was experiencing significant growth and diversification. Here are some key trends:
Expansion of Charging Infrastructure: Governments, businesses, and utilities worldwide are investing in expanding EV charging infrastructure to support the growing number of electric vehicles on the road. This includes the installation of more public charging stations in urban areas, along highways, and in workplaces.
Fast Charging Technology: There's a notable trend towards faster charging technologies, such as DC fast chargers, which can provide a significant amount of charge in a short amount of time. Improvements in charging speeds are critical for reducing charging times and increasing the convenience of EV ownership.
Home Charging Solutions: With more people opting for electric vehicles, there's a growing demand for home charging solutions. This includes the installation of Level 2 chargers in residential properties, as well as the integration of smart charging technology that allows EV owners to monitor and control charging remotely.
Integration with Renewable Energy: There's an increasing focus on integrating EV charging infrastructure with renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. This not only helps reduce the carbon footprint of electric vehicles but also makes charging more sustainable and cost-effective in the long run.
Smart Charging Technology: Smart charging solutions, including software platforms and mobile apps, are becoming more prevalent. These technologies enable EV owners to schedule charging times, optimize energy usage, and access real-time charging information from their smartphones or other devices.
Wireless Charging: While still in the early stages, there's growing interest in wireless charging technology for electric vehicles. Wireless charging eliminates the need for physical cables and connectors, offering greater convenience and ease of use, especially for applications like electric taxis and autonomous vehicles.
Partnerships and Collaborations: Companies across various industries are forming partnerships and collaborations to accelerate the deployment of EV charging infrastructure. This includes collaborations between automakers, energy companies, technology firms, and governments to develop and implement comprehensive charging solutions.
Overall, the trend of EV chargers is towards greater accessibility, convenience, and sustainability, driven by advancements in technology, supportive government policies, and increasing consumer demand for electric vehicles.
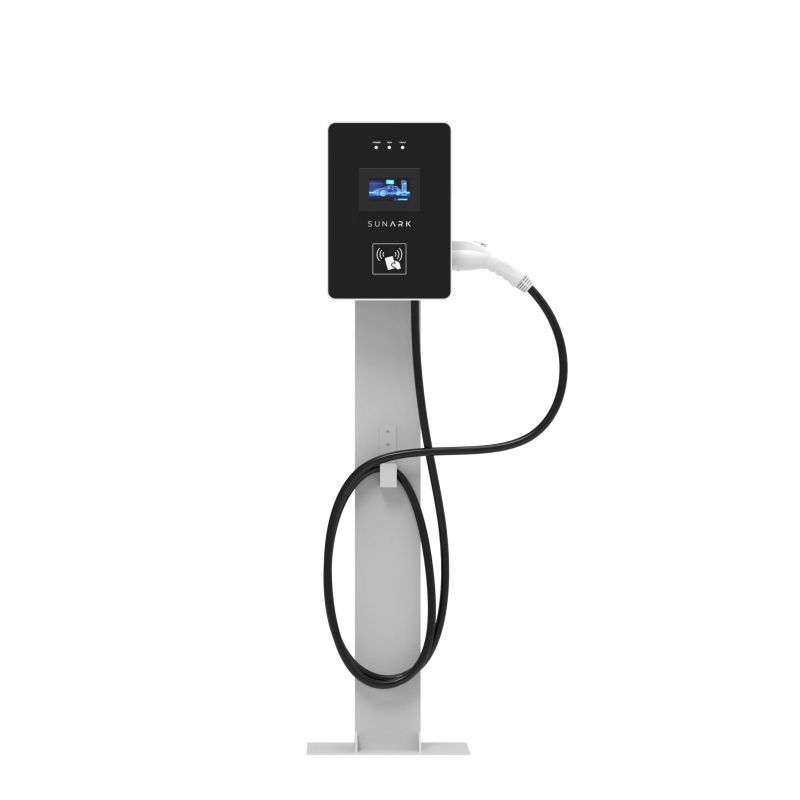

Here are the main types of EV chargers:
Level 1 Charger: These chargers typically use a standard household electrical outlet (120 volts AC) and provide the slowest charging speeds. Level 1 chargers are commonly used for overnight charging at home and are included with most electric vehicles for basic charging needs.
Level 2 Charger: Level 2 chargers operate at higher power levels than Level 1 chargers, typically using 240 volts AC power. They can charge an electric vehicle much faster than Level 1 chargers, making them suitable for home installation, workplaces, and public charging stations.
DC Fast Charger (Level 3 Charger): DC Fast Chargers, also known as Level 3 chargers, provide the fastest charging speeds and are primarily used for public charging stations along highways and in commercial areas. These chargers supply direct current (DC) power directly to the vehicle's battery, bypassing the vehicle's onboard charger, allowing for rapid charging.
EV chargers vary in terms of their connector types, with the most common being:
J1772 Connector: Standard for Level 1 and Level 2 charging in North America.
Type 2 Connector (IEC 62196): Common in Europe for both AC and DC charging.
CCS (Combined Charging System): A combined AC and DC charging connector primarily used in Europe and North America.
CHAdeMO: A DC fast charging connector primarily used by Japanese and some European manufacturers.
Tesla Connector: Proprietary connector used by Tesla for both AC and DC charging, though adapters are available for use with other charger types.

what is DC charge station?
A DC charge station, also known as a DC fast charger or Level 3 charger, is a type of electric vehicle (EV) charging station that is capable of providing high-power direct current (DC) to quickly recharge the battery of an electric vehicle. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which supply alternating current (AC) and are commonly found in homes and workplaces, DC fast chargers are primarily located in public charging stations along highways, in commercial areas, and at EV service stations.
DC fast chargers are designed to deliver a much higher charging power compared to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, enabling EVs to recharge their batteries to a significant percentage of capacity in a relatively short amount of time. This makes DC fast chargers particularly useful for long-distance travel and situations where EV drivers require a quick recharge to continue their journey.
Here are some key features of DC charge stations:
High Charging Power: DC fast chargers can deliver charging power ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW or more, depending on the charger's capacity and the capabilities of the EV being charged. This allows for rapid charging and significantly reduces the time required to recharge an EV compared to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers.
Direct Current Supply: Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which convert AC power from the grid to DC power using the onboard charger of the EV, DC fast chargers supply DC power directly to the vehicle's battery. This bypasses the vehicle's onboard charger and allows for faster charging rates.
Compatibility: DC fast chargers are typically equipped with multiple connector types to accommodate different EV models and charging standards. Common connector types include CCS (Combined Charging System), CHAdeMO, and Tesla Supercharger connectors. Some DC fast chargers also support multiple power levels to cater to a wide range of EVs.
Public Charging Infrastructure: DC fast chargers are an essential component of public EV charging infrastructure, providing EV drivers with convenient access to fast charging facilities while on the go. They are often located at rest areas, service stations, shopping centers, and other high-traffic areas to support long-distance travel and promote EV adoption.
Overall, DC charge stations play a critical role in enabling the widespread adoption of electric vehicles by addressing concerns about range anxiety and providing fast and convenient charging solutions for EV drivers.
FAQs:
Q1: Do you support OEM/ODM?
A:Definitely, OEM&ODM service is supported with a certain quantity,including customize logo,package and label;
Q2: What's the production time?
A: The production time is normally 15 working days. but we will always prepare some stocks for popular models.
Q3: Can you provide DDP service?
A:Yes, if you are a personal customer and don't want to deal with the customs, we can provide DDP service to your address.
Q4: What about the warranty and how to claim?
A: Warranty period are 5 years since you receive the product, our professional after-sales team will deal with all warranty issues.