It's important to note that the availability of chargers may vary depending on your location and the infrastructure in place. Additionally, newer charging technologies may emerge over time, so it's always good to stay updated with the latest developments in EV charging technology.
Standard:
SAE Standard / IEC StandardConnector type:
Type 1 / Type 2Connector Mechanical Operating Life:
≥10000 times
EV chargers can be categorized into types based on their levels and connection methods Here are the main categories1. Level 1 Chargers: These are the most basic chargers and typically included with electric. Level 1 chargers charging through a standard 120V AC household outlet. They deliver a charging rate of approximately 2-5 miles of range per hour, making them suitable for overnight charging.
Level 2 Chargers: Level 2 chargers use a 240V AC power supply, similar to what is used for appliances like electric dryers. They offer a faster charging rate of around 10-30 miles of range per hour, depending on the vehicle and charger capacity. Level 2 chargers are commonly used in residential, workplace, and public charging stations.
DC Fast Chargers: Also known as Level 3 chargers or "fast chargers," DC fast chargers provide significantly faster charging speeds compared to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. They use direct current (DC) power instead of alternating current (AC), allowing them to charge the battery directly. DC fast chargers can deliver up to 60-80% of a battery's capacity in under 30 minutes, depending on the vehicle and charger specifications. These chargers are typically found at public charging stations along highways and major routes.
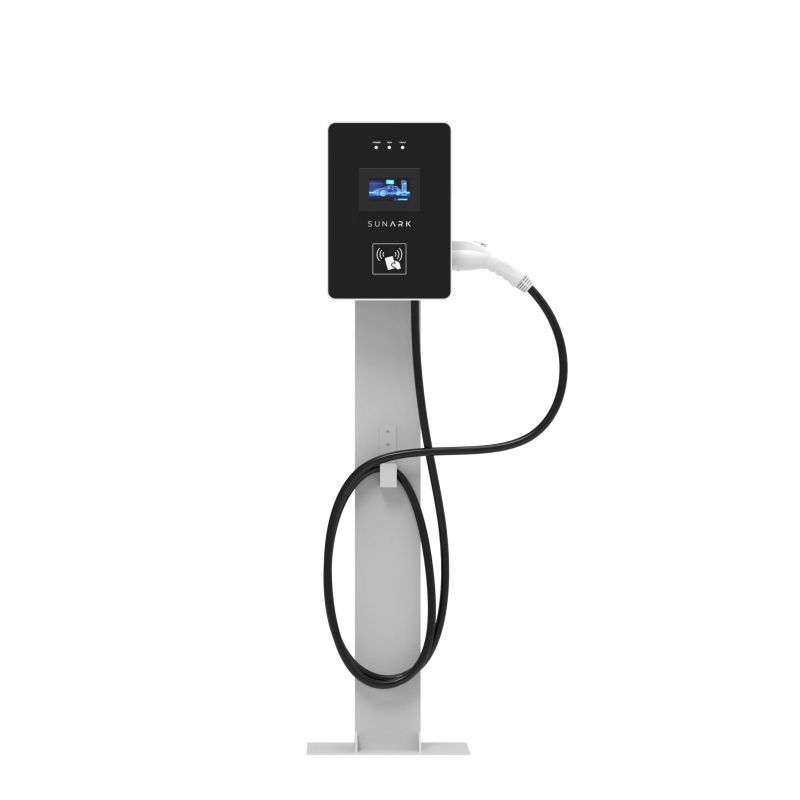

What does AC EV Charger Include?
AC (alternating current) EV chargers include the following components:
Power Supply: AC chargers require a source of electrical power, typically from the power grid, to convert AC power to the appropriate voltage and current to charge the EV.
Connector: The charger is equipped with a connector that plugs into the EV. The type of connector may vary depending on the region and standards followed. Common types include Type 1 (SAE J1772) or Type 2 (Mennekes).
Charging Cable: The charging cable connects the charger to the EV. It carries the electricity from the charger to the vehicle's battery.
Control Unit: AC chargers have a control unit to manage the charging process. It regulates the flow of electricity, monitors the battery's state of charge, and ensures safe and efficient charging.
Charging Station: Some AC chargers are standalone units, while others are part of a charging station that may include multiple charging points. A charging station often provides additional features such as user authentication, billing, and monitoring capabilities.
Charging Modes: AC chargers support different charging modes. The most common modes are Level 1 and Level 2 charging. Level 1 chargers utilize a standard household outlet and typically provide a lower charging rate, while Level 2 chargers require a higher-power dedicated circuit and offer faster charging.

DC EV chargers, also known as fast chargers or Level 3 chargers, include the following components:
Charging Station: The charging station is the main unit that provides the power and charging capabilities for the electric vehicle. It typically consists of power electronics, high-voltage connectors, and a user interface.
Power Conversion System: The power conversion system converts AC (alternating current) electricity from the grid into DC (direct current) electricity that is compatible with the electric vehicle's battery.
Charging Cable: The charging cable connects the charging station to the electric vehicle. It is designed to carry high current and is equipped with appropriate connectors to facilitate a secure and efficient charging process.
Communication and Control System: DC chargers incorporate communication and control systems to interact with the electric vehicle and manage the charging process. This includes protocols for authorization, data exchange, and monitoring.
Safety Features: DC chargers are equipped with safety features to ensure reliable and safe charging. These may include features such as ground fault protection, overcurrent protection, and thermal monitoring to prevent overheating.
Monitoring EV chargers involves various methods, including:
Charger Management Software: Many charging station providers offer software platforms that allow users to monitor and manage their EV chargers remotely. These platforms provide real-time data on charging sessions, energy usage, and payment processing.
Mobile Apps: Some charging station manufacturers provide companion mobile applications that allow users to monitor their charging sessions, check the status of chargers, and receive notifications or alerts.
Networked Charging Stations: Charging stations connected to a network can be monitored centrally by charging station operators or service providers. They can access data on charging status, energy consumption, and any faults or maintenance requirements.
Energy Management Systems: In commercial or public charging installations, energy management systems may be used to monitor and optimize the charging process. These systems can gather data from multiple chargers, manage charging schedules, and balance energy demand.
FAQs:
Q1: Do you support OEM/ODM?
A:Definitely, OEM&ODM service is supported with a certain quantity,including customize logo,package and label;
Q2: What's the production time?
A: The production time is normally 15 working days. but we will always prepare some stocks for popular models.
Q3: Can you provide DDP service?
A:Yes, if you are a personal customer and don't want to deal with the customs, we can provide DDP service to your address.
Q4: What about the warranty and how to claim?
A: Warranty period are 5 years since you receive the product, our professional after-sales team will deal with all warranty issues.