The specific components and features of AC/DC charging stations can vary depending on the manufacturer, charging standards supported (e.g., CHAdeMO, CCS, or Tesla Supercharger), and the power output capabilities (e.g., Level 2 or Level 3 fast charging).
Standard:
SAE Standard / IEC StandardConnector type:
Type 1 / Type 2Connector Mechanical Operating Life:
≥10000 times
The trend of charging stations, especially for electric vehicles (EVs), has been on the rise in recent years. Here are some key trends in the development of charging stations:
Increased Deployment: The number of charging stations is growing globally, driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles. Governments, businesses, and individuals are investing in charging infrastructure to support the expanding EV market.
Fast Charging: There is a growing demand for fast-charging solutions to reduce the charging time of EVs. High-power charging stations (DC fast chargers) have become more prevalent, enabling EVs to be charged in a matter of minutes rather than hours.
High-Power Charging Networks: Charging networks have emerged to improve accessibility and allow EV drivers to travel longer distances. These networks often include fast-charging stations strategically located along major highways and in urban areas.
Integration with Renewable Energy: Charging stations are increasingly being integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. This enables the charging process to be more environmentally friendly and reduces the overall carbon footprint of EVs.
Smart Charging and Grid Integration: The integration of charging infrastructure with smart grid technologies allows for optimized charging patterns. This includes features like load management, demand response, and dynamic pricing, which can help balance the electricity grid and reduce strain during peak charging periods.
Charging Station Diversity: To cater to various user needs, charging stations are becoming more diverse in terms of their capabilities and designs. This includes different charging speeds (Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging), various connector types (CHAdeMO, CCS, Tesla Supercharger, etc.), and the integration of amenities like parking spaces, convenience stores, and rest areas.
Wireless Charging: Wireless charging technology is being developed and deployed, allowing EVs to charge without the need for physical cables. This technology relies on electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between the charging pad and the vehicle, providing convenience and reducing wear and tear on physical connectors.
Overall, the trend of charging stations is focused on expanding infrastructure, improving charging speeds, integrating with renewable energy, and advancing smart grid technologies to meet the growing demand for electric vehicles.
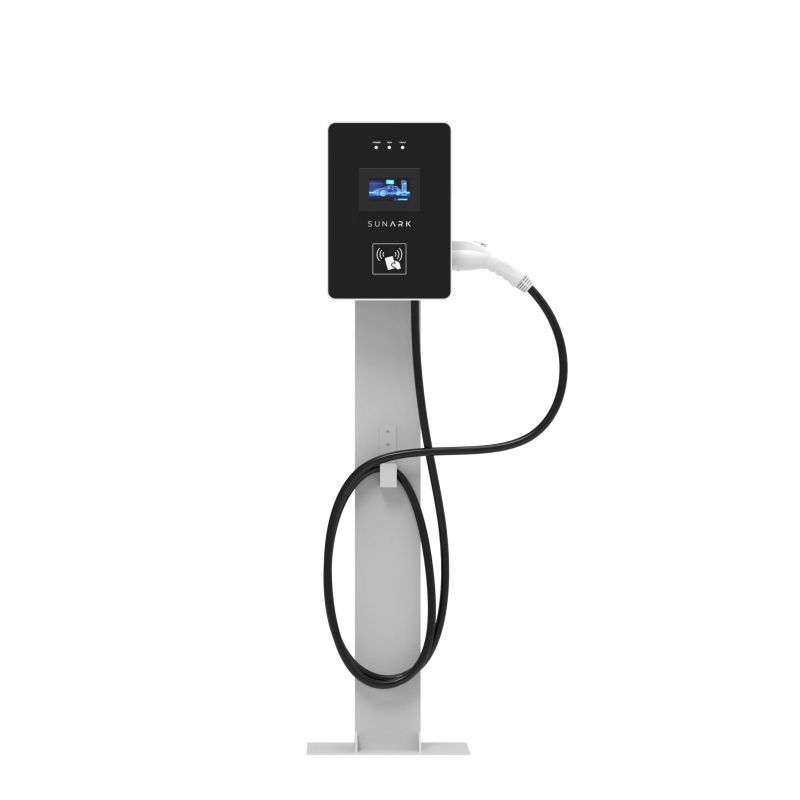

An AC/DC charging station for electric vehicles typically the following components:
Power Supply: The charging station is connected to the electrical grid to provide the necessary power for charging the electric vehicle.
Charging Interface: The charging interface is where the electric vehicle is physically connected to the charging station. It typically includes a plug or socket that matches the vehicle's charging port.
Control and Communication Unit: This unit manages the charging process, monitors the charging status, and communicates with the electric vehicle and the grid. It handles protocols such as authentication, power control, and safety features.
Power Electronics: The power electronics convert the AC power from the grid to the appropriate DC voltage required by the electric vehicle's battery. It regulates the charging current and voltage to ensure safe and efficient charging.
Safety Features: AC/DC charging stations include various safety features to protect against potential hazards, such as ground fault protection, over-current protection, over-voltage protection, and short-circuit protection.
Metering and Billing: In some cases, charging stations may incorporate meters to measure the amount of energy consumed for billing purposes. This allows for accurate tracking of charging costs and usage.
Networking and Connectivity: Charging stations often have networking capabilities to enable remote monitoring, control, and software updates. They can be connected to a central management system or network for monitoring multiple charging stations simultaneously.

Here are some notable features and trends related to DC charge stations:
High charging power: DC fast chargers are designed to deliver high-power charging to EVs.
Compatibility with multiple standards: DC charge stations support different charging standards to cater to various EV models.
Rapid charging times: The primary advantage of DC fast chargers is their ability to provide a substantial amount of energy to EVs in a relatively short time.
Increasing charging power: As technology advances, DC charge stations are continually being developed to deliver even higher charging power.
Enhanced connectivity and integration: DC fast chargers are often equipped with advanced connectivity features
Expansion of charging networks: There is a growing trend of expanding public DC charge station networks, making long-distance travel in electric vehicles more feasible.
Integration with renewable energy sources: With the increasing adoption of renewable energy, DC charge stations are being integrated with solar or wind power installations.
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities: Some DC fast chargers are designed with V2G technology, enabling bidirectional power flow between EVs and the power grid.
High-power charging corridors: The concept of high-power charging corridors is gaining momentum, especially in regions with long driving distances or heavy EV adoption.
Monitoring EV chargers involves various methods, including:
Charger Management Software: Many charging station providers offer software platforms that allow users to monitor and manage their EV chargers remotely. These platforms provide real-time data on charging sessions, energy usage, and payment processing.
Mobile Apps: Some charging station manufacturers provide companion mobile applications that allow users to monitor their charging sessions, check the status of chargers, and receive notifications or alerts.
Networked Charging Stations: Charging stations connected to a network can be monitored centrally by charging station operators or service providers. They can access data on charging status, energy consumption, and any faults or maintenance requirements.
Energy Management Systems: In commercial or public charging installations, energy management systems may be used to monitor and optimize the charging process. These systems can gather data from multiple chargers, manage charging schedules, and balance energy demand.
FAQs:
Q1: Do you support OEM/ODM?
A:Definitely, OEM&ODM service is supported with a certain quantity,including customize logo,package and label;
Q2: What's the production time?
A: The production time is normally 15 working days. but we will always prepare some stocks for popular models.
Q3: Can you provide DDP service?
A:Yes, if you are a personal customer and don't want to deal with the customs, we can provide DDP service to your address.
Q4: What about the warranty and how to claim?
A: Warranty period are 5 years since you receive the product, our professional after-sales team will deal with all warranty issues.