A charge station, also known as an electric vehicle (EV) charging station or an EV charging point, is a dedicated infrastructure that supplies electricity to recharge electric vehicles. It is similar to a fuel station for conventional vehicles but specifically designed for chargings.
Standard:
SAE Standard / IEC StandardConnector type:
Type 1 / Type 2Connector Mechanical Operating Life:
≥10000 times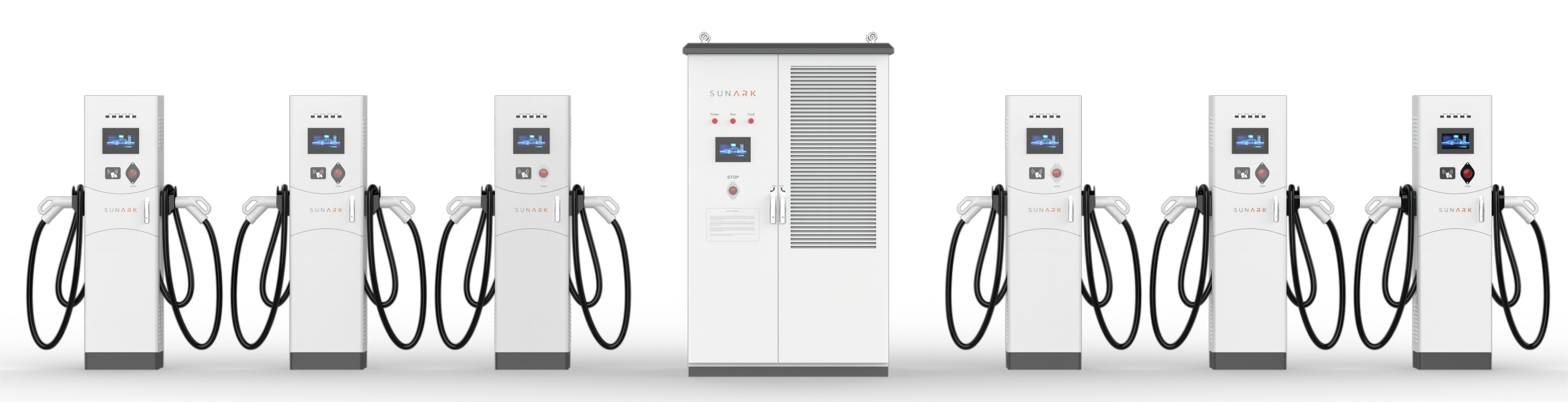
Charge stations come in different types and can vary in charging speed and capabilities. Here are a few common types of charge stations:
Level 1 Charger: This is the slowest type of charger and typically comes with the vehicle itself. It uses a standard household outlet (120 volts AC) and provides a charging rate of around 2-5 miles of range per hour of charging. Level 1 chargers are primarily used for overnight charging or when longer charging times are acceptable.
Level 2 Charger: Level 2 chargers use a 240-volt AC power supply and provide faster charging compared to Level 1 chargers. They typically deliver charging rates from 10 to 60 miles of range per hour, depending on the vehicle and charger capacity. Level 2 chargers are commonly installed in homes, workplaces, public parking lots, and other locations where EVs park for an extended period.
DC Fast Charger (also known as Level 3 Charger): DC Fast Chargers are the fastest charging stations currently available. They provide high-voltage DC power directly to the vehicle's battery, bypassing the vehicle's onboard charger. DC Fast Chargers can charge an EV from 0 to 80% in around 20-30 minutes, depending on the vehicle and charger capabilities. These chargers are typically found along major highways, rest areas, and commercial areas to facilitate long-distance travel and quick recharging.
It's important to note that different electric vehicles have different charging capabilities, and not all vehicles can utilize the full charging speed provided by each type of charger. Additionally, the charging infrastructure may vary depending on the country or region you are in. It's always recommended to consult your specific vehicle's manual or contact the charging station operator for information on compatible chargers and charging speeds.
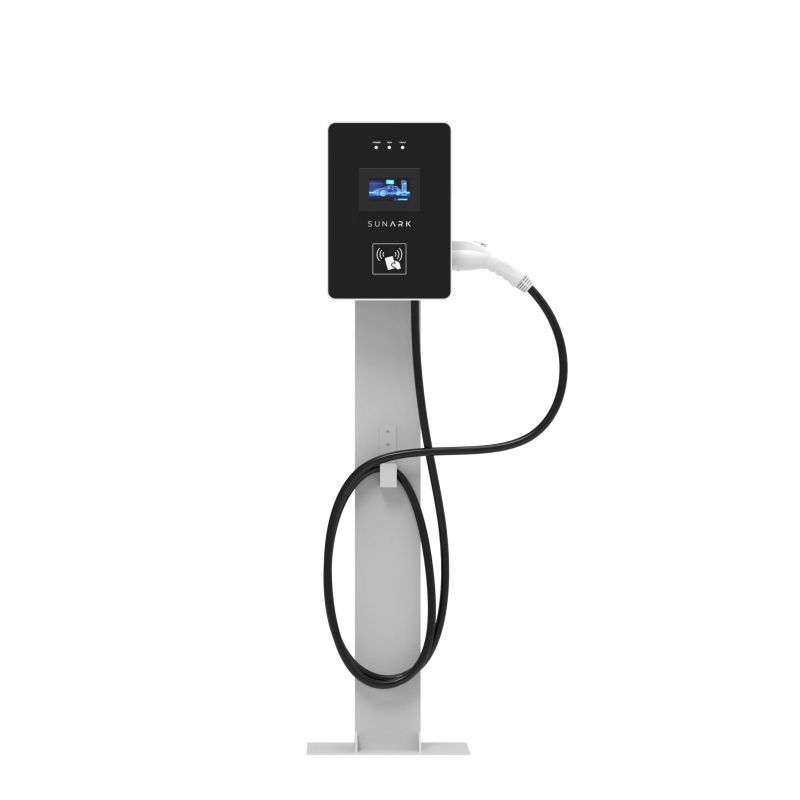

What is AC EV charger mean?
An AC charger, also known as an alternating current charger, is a device used to charge electric vehicles (EVs) by converting AC power from the electrical grid into DC (direct current) power that can be stored in the vehicle's battery.
AC chargers typically come in different power levels, commonly categorized as Level 1 and Level 2 chargers.
Level 1 chargers: These chargers operate on a standard 120-volt AC power outlet, commonly found in households. They provide a slower charging rate compared to higher-powered chargers, typically delivering around 2 to 5 miles of range per charging hour.
Level 2 chargers: These chargers require a dedicated 240-volt AC power supply, similar to what is used for large appliances like electric dryers. Level 2 chargers provide faster charging rates, generally ranging from 10 to 60 miles of range per hour, depending on the EV's battery capacity and the charger's power output.

What is main port of a DC charge station?
The main point of a DC charge station, also known as a DC fast charger or DC rapid charger, is to provide a high-power charging solution for electric vehicles (EVs). Unlike AC chargers, which convert alternating current (AC) from the electrical grid to the direct current (DC) used by EV batteries, DC fast chargers supply DC power directly to the vehicle's battery.
The primary advantage of DC fast charging is its ability to provide significantly faster charging times compared to AC charging. By providing a high-power DC electricity flow, these chargers can recharge an EV's battery much more quickly. Depending on the charging station's power rating and the EV's capability, it is possible to attain an 80% charge in as little as 20-30 minutes, making it convenient for longer trips or quick top-ups.
DC charge stations are typically installed at public locations such as rest areas, service stations, or along highways, where drivers can access fast charging to extend their driving range. They play a crucial role in expanding the usability and practicality of electric vehicles, offering a convenient and efficient solution for EV owners who need to charge on the go.
How to use the monitoring APP?
Centralized Monitor System: EV chargers can be connected to a centralized monitoring system that allows operators or administrators to remotely monitor the charging status, energy consumption, and any faults or abnormalities of the chargers.
Mobile Applications: Many EV charger manufacturers provide mobile applications that allow users to monitor and control the charging process.
Website: Some EV charging networks offer web portals where users can log in to monitor their charging sessions, view charging history, and access other relevant information.
RFID or NFC Card: EV chargers can be equipped with RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) or NFC (Near Field Communication) card readers.
Display Screens: Many EV chargers have built-in display screens that show real-time charging information, such as charging power, charging time
It's worth noting that AC chargers are generally slower compared to DC fast chargers, which can be a disadvantage when fast recharging is needed. However, for everyday charging needs and regular use, AC chargers offer a convenient and cost-effective solution.
FAQs:
Q1: Do you support OEM/ODM?
A:Definitely, OEM&ODM service is supported with a certain quantity,including customize logo,package and label;
Q2: What's the production time?
A: The production time is normally 15 working days. but we will always prepare some stocks for popular models.
Q3: Can you provide DDP service?
A:Yes, if you are a personal customer and don't want to deal with the customs, we can provide DDP service to your address.
Q4: What about the warranty and how to claim?
A: Warranty period are 5 years since you receive the product, our professional after-sales team will deal with all warranty issues.