EV chargers typically support a variety of charging protocols, depending on the type and level of charger.
It's important to note that not all EV chargers support all the above-mentioned protocols. The compatibility of a charging station with specific charging protocols depends on the manufacturer and the intended market or region.
Standard:
SAE Standard / IEC StandardConnector type:
Type 1 / Type 2Connector Mechanical Operating Life:
≥10000 times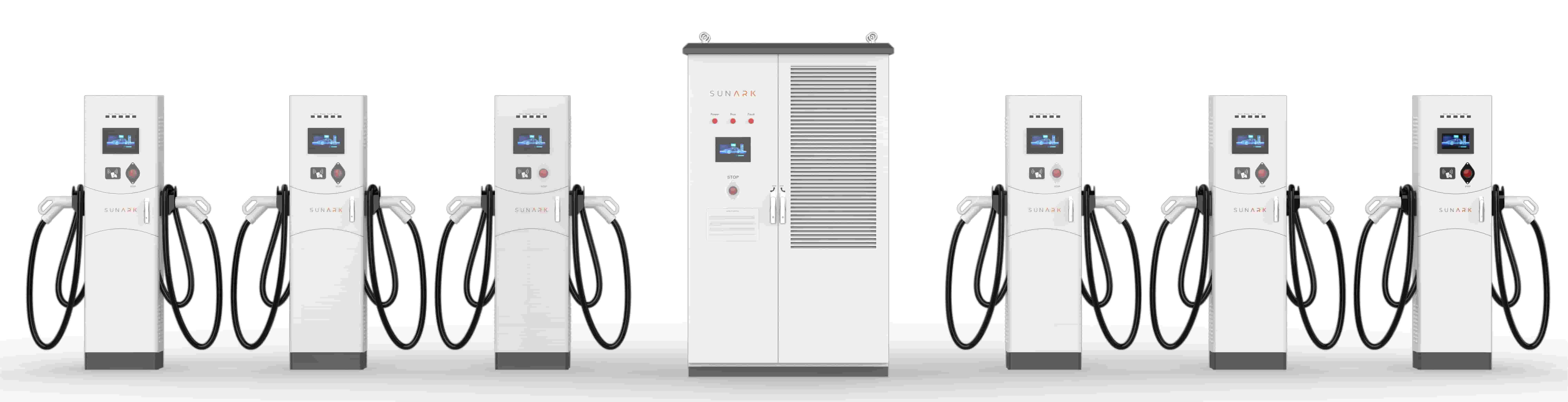
The most common charging protocols for AC chargers include:
J1772 (SAE J1772): This is a standard charging protocol used in North America and some other regions. It supports Level 1 (120V AC, typically used for overnight charging) and Level 2 (240V AC, faster charging) charging.
Type 2 (IEC 62196-2): This is a widely used European standard charging protocol. It supports both single-phase (230V AC) and three-phase (400V AC) charging, providing faster charging speeds.
Mennekes: This is the popular brand name for Type 2 connectors and charging infrastructure used in Europe.
It's worth mentioning that these protocols define the physical connector and communication standards between the charger and the electric vehicle. The actual charging power (kW) and charging speed depend on factors such as the vehicle's onboard charger capabilities, battery capacity, and the power rating of the charging station.
On the other hand, for DC fast chargers, commonly known as rapid chargers, the following charging protocols are commonly used:
CHAdeMO: Developed by the CHAdeMO Association, this protocol is primarily used by Japanese and Korean automakers. It enables high-power DC charging for compatible vehicles.
CCS (Combined Charging System): This charging protocol combines the use of the J1772 AC connector and an additional two DC pins. It supports both AC and DC charging and is widely adopted by European and American automakers.
Tesla Supercharger: Tesla's proprietary charging protocol and connector are used exclusively for Tesla vehicles. They support high-power DC charging and are accessible through Tesla's Supercharger network.
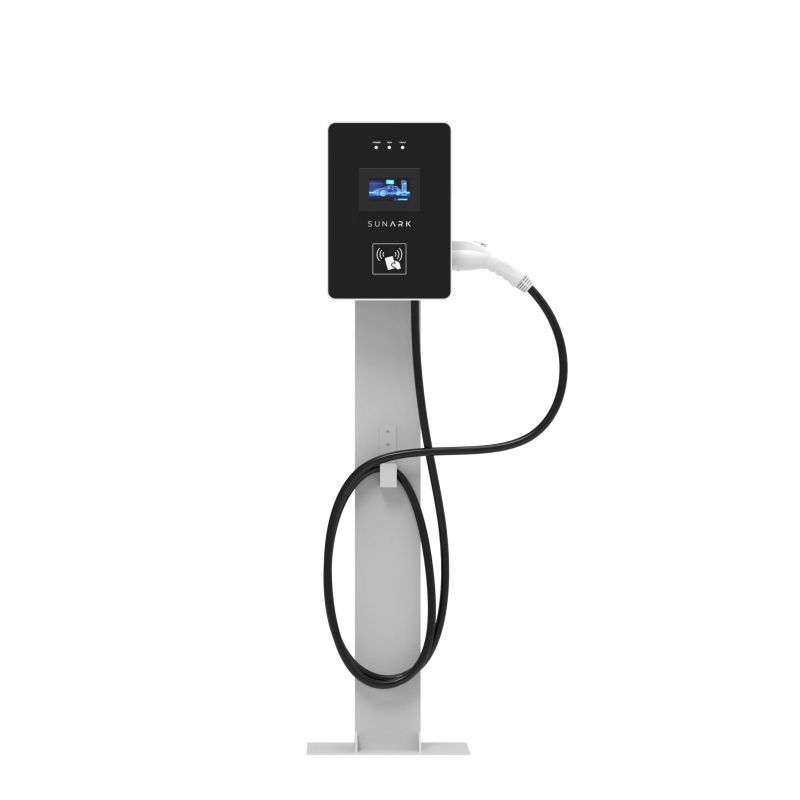

What does AC EV Charger Include?
AC (alternating current) EV chargers include the following components:
Power Supply: AC chargers require a source of electrical power, typically from the power grid, to convert AC power to the appropriate voltage and current to charge the EV.
Connector: The charger is equipped with a connector that plugs into the EV. The type of connector may vary depending on the region and standards followed. Common types include Type 1 (SAE J1772) or Type 2 (Mennekes).
Charging Cable: The charging cable connects the charger to the EV. It carries the electricity from the charger to the vehicle's battery.
Control Unit: AC chargers have a control unit to manage the charging process. It regulates the flow of electricity, monitors the battery's state of charge, and ensures safe and efficient charging.
Charging Station: Some AC chargers are standalone units, while others are part of a charging station that may include multiple charging points. A charging station often provides additional features such as user authentication, billing, and monitoring capabilities.
Charging Modes: AC chargers support different charging modes. The most common modes are Level 1 and Level 2 charging. Level 1 chargers utilize a standard household outlet and typically provide a lower charging rate, while Level 2 chargers require a higher-power dedicated circuit and offer faster charging.

what does DC EV charge include?
Power Conversion System: The charger has a power conversion system that takes the incoming AC power from the electrical grid and converts it to DC power suitable for charging the vehicle's battery.
Charging Connector: The charger is equipped with a charging connector or cable that physically connects the charger to the electric vehicle. The connector type may vary depending on the region and the vehicle's charging capabilities, such as CHAdeMO, CCS (Combined Charging System), or Tesla's proprietary connector.
Charging Station/Unit: This is the main housing or enclosure that contains the power conversion system and other electronic components. It provides protection, controls, and monitoring functionalities for the charging process.
Cooling System: DC fast chargers generate a significant amount of heat due to the high power demands during fast charging. To prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance, they usually incorporate cooling systems such as fans or liquid cooling systems.
Communication and Control System: DC chargers often include a communication interface, such as Ethernet, cellular connectivity, or Wi-Fi, to enable communication between the charger and the electric vehicle. This allows for various functionalities like authentication, monitoring, and remote control.
User Interface: Typically, a DC charger includes a user interface, such as an LCD screen or touch panel, to provide information to users and allow them to interact with the charger. It may display charging status, data, and instructions, and can include buttons or touch controls for operation.
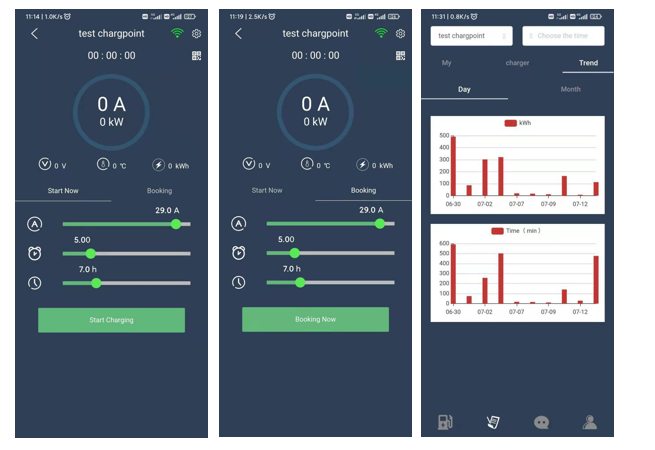
How to monitor EV chargers?
Power Output: Monitor the power output of the charger to ensure it aligns with the advertised capabilities. This includes checking the voltage and current levels to ensure they meet the intended charging rate.
Charging Status: Monitor the charging status of individual charging sessions, including whether the charger is actively charging, in standby mode, or not functioning at all. This information helps identify any potential issues, such as charging failures or stalls.
Charging Sessions: Keep track of charging sessions by recording information such as start time, end time, charging duration, energy consumption, and total cost. This data helps analyze usage patterns and detect abnormalities.
Fault Detection: Monitor for any potential faults or errors reported by the charger. This includes checking for charging circuit failures, communication errors, or safety-related issues.
User Authentication: Ensure that the chargers maintain a secure authentication mechanism to verify the identity of users. Monitoring this aspect helps identify any unauthorized access attempts or security breaches.
Connectivity and Communication: Monitor the connectivity and communication status of the chargers to ensure they are properly linked to management systems or networks. This includes checking for network outages, communication errors, or connectivity interruptions.
Remote Control and Management: Monitor the ability to remotely control and manage the chargers, including starting or stopping charging sessions, adjusting charging parameters, or updating firmware. This allows for efficient maintenance and troubleshooting.
Energy Usage and Billing: Monitor the energy consumption of the chargers to accurately bill users or track total energy usage. This may involve integrating with billing systems or metering devices to collect and analyze relevant data.
Maintenance and Diagnostics: Keep track of maintenance schedules and perform regular diagnostics to identify any potential issues or required maintenance tasks. This helps ensure the chargers are functioning optimally and reduces downtime.
Reporting and Analytics: Generate reports and perform data analytics to gain insights into charger usage, performance trends, and energy consumption patterns. This information can help optimize charger placement, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall charging infrastructure.
FAQs:
Q1: Do you support OEM/ODM?
A:Definitely, OEM&ODM service is supported with a certain quantity,including customize logo,package and label;
Q2: What's the production time?
A: The production time is normally 15 working days. but we will always prepare some stocks for popular models.
Q3: Can you provide DDP service?
A:Yes, if you are a personal customer and don't want to deal with the customs, we can provide DDP service to your address.
Q4: What about the warranty and how to claim?
A: Warranty period are 5 years since you receive the product, our professional after-sales team will deal with all warranty issues.