By integrating solar panels, batteries, and grid interaction capabilities into one device, SunArk hybrid solar inverter provides a comprehensive solution for managing and optimizing the use of solar energy in a solar power system
Brand:
SunArkBrand:
SunArkModel name:
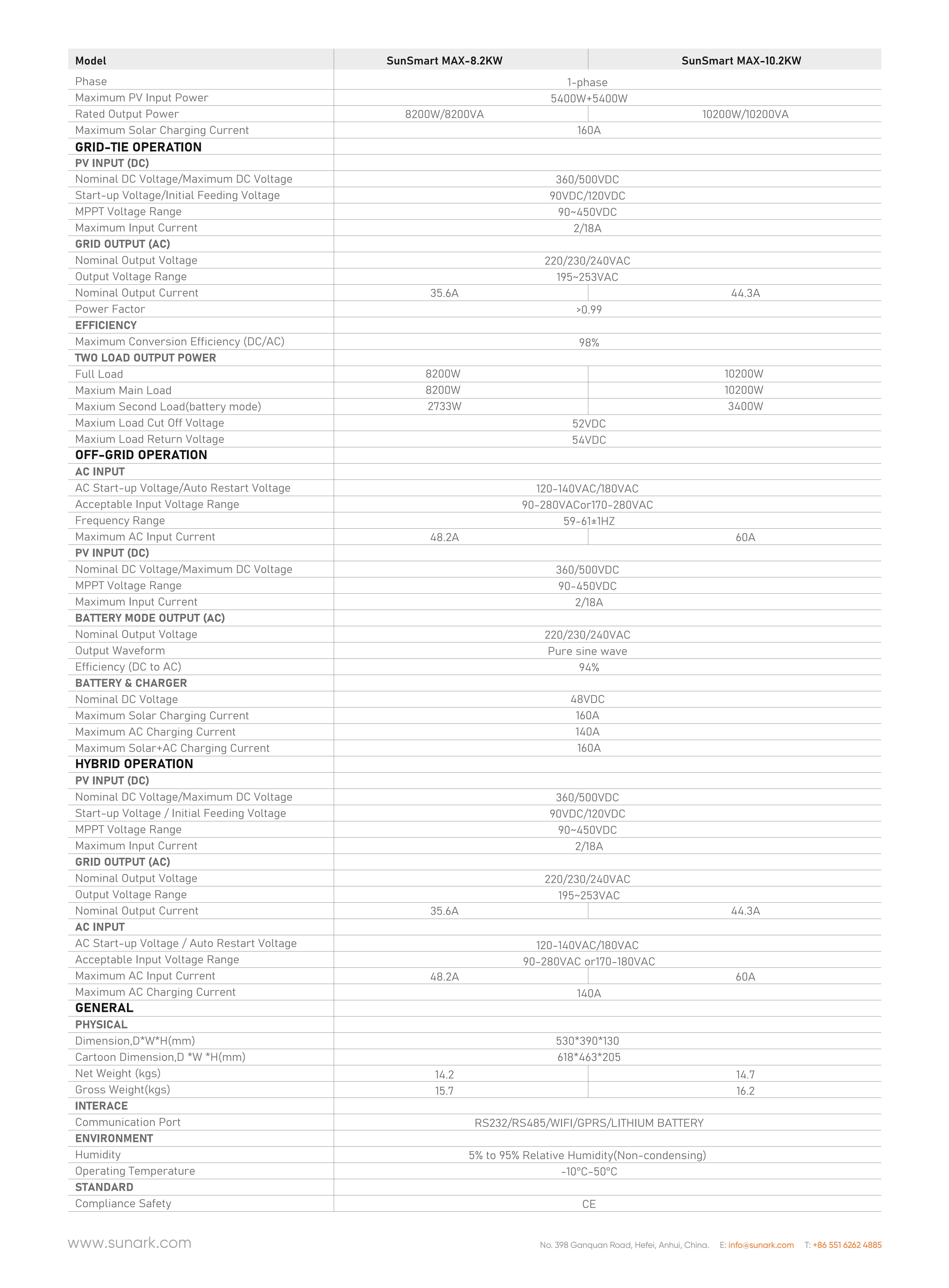
SunSmart MAX-8.2KW / SunSmart MAX-10.2KWMax PV power:
10200WMPPT voltage range:
30~400VDCRated output power:
10200WOutput voltage:
230VAC±5%The datasheet of SunArk SunSmart MAX series 10200VA at below:
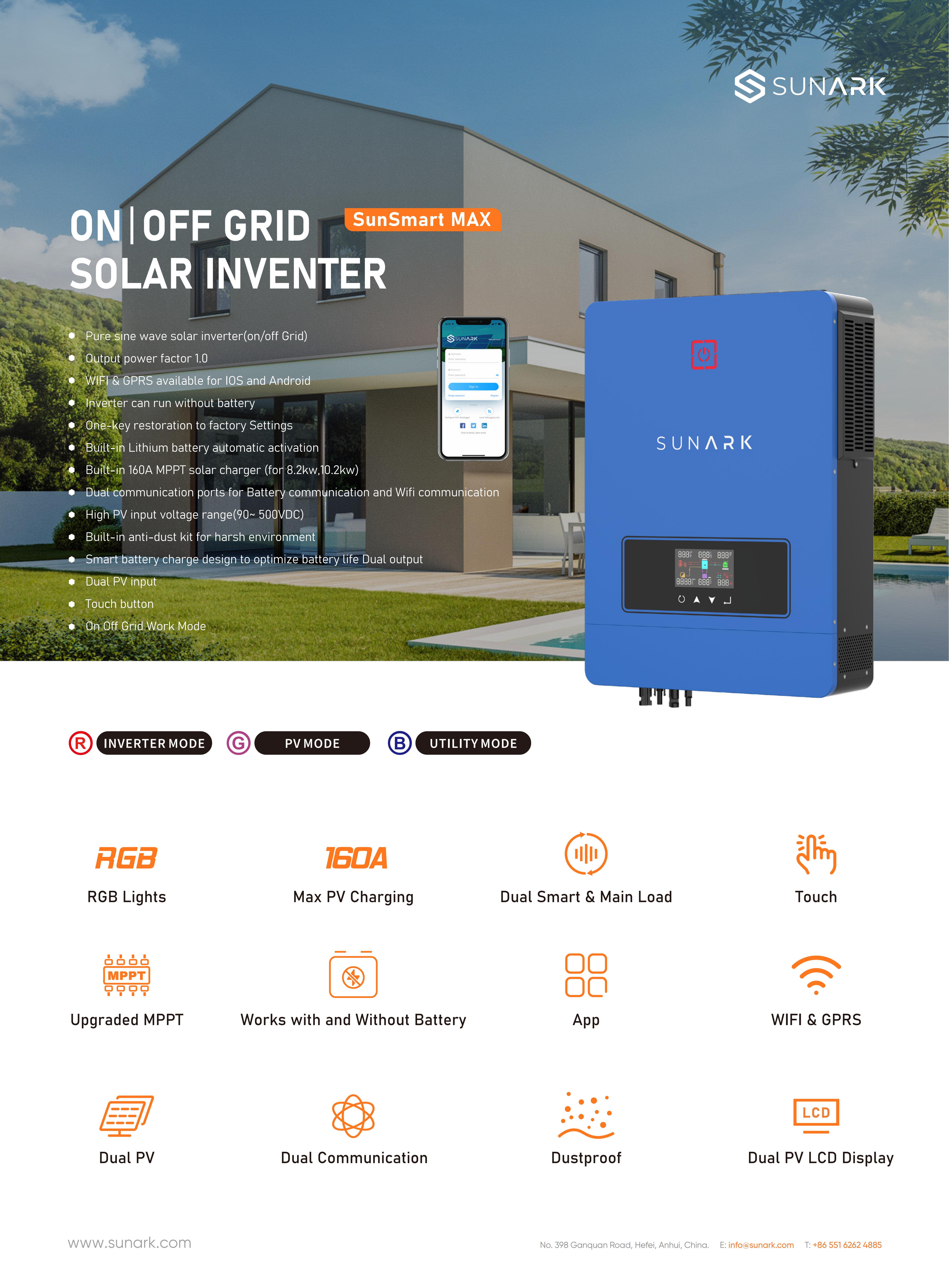

A hybrid solar inverter is a key component of a hybrid solar power system. It is responsible for managing the flow of electricity between solar panels, batteries, and the electrical grid, optimizing energy usage and ensuring a reliable power supply. Here is a description of how a hybrid inverter works in a solar system:
1. Solar Power Conversion: The hybrid inverter receives the DC electricity generated by the solar panels. It converts this DC electricity into AC electricity, which is the standard form of electricity used in most households and buildings.
2. Grid Interaction: The hybrid inverter monitors the energy demand in the building and determines whether to use solar power, grid power, or a combination of both to meet the demand. If there is excess solar power available, it can be fed back into the electrical grid for credits or to offset future electricity consumption.
3. Battery Charging: In a hybrid solar system, any surplus solar power that is not immediately consumed can be stored in batteries for later use. The hybrid inverter controls the battery charging process, regulating the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries. It ensures that the batteries are charged efficiently and prevents overcharging or undercharging, which can damage the batteries.
4. Battery Discharging: When there is a demand for electricity but the solar panels are not producing enough power (e.g., during the night or on cloudy days), the hybrid inverter draws electricity from the batteries. It converts the DC power stored in the batteries back into AC power and supplies it to the building's electrical system.
5. Energy Management: The hybrid inverter optimizes energy usage and prioritizes the utilization of solar power and stored energy. It continuously monitors the amount of solar power being generated, the battery charge level, and the electricity consumption in the building. By analyzing these factors, it determines the most efficient combination of solar power, battery power, and grid power to minimize reliance on grid electricity and maximize self-consumption of renewable energy.
6. Monitoring and Control: Hybrid inverters often come with monitoring and control features that allow users to monitor the performance of the solar system, battery status, and energy production and consumption. This information can be accessed through a display panel on the inverter or through a smartphone app or online platform. Users can also adjust the settings of the inverter, such as the charging and discharging parameters, remotely.
Overall, the hybrid solar inverter acts as the brain of the hybrid solar system, regulating the flow of electricity and optimizing energy usage to ensure a reliable and efficient power supply. It enables seamless integration of solar power, battery storage, and grid electricity, offering increased energy independence, reduced reliance on the grid, and potential cost savings

A hybrid solar inverter is a crucial component of a solar power system that incorporates both solar panels and energy storage, typically in the form of batteries. Its primary function is to manage the flow of electricity between the solar panels, batteries, and the electrical grid. Here's a step-by-step explanation of how a hybrid solar inverter works in a solar system:
Solar Power Generation: The solar panels generate DC (direct current) electricity from sunlight. This DC electricity is then sent to the hybrid solar inverter.
1. Conversion to AC: The hybrid inverter converts the DC electricity from the solar panels into AC (alternating current) electricity, which is the standard form of electricity used in homes and buildings.
2. Power Consumption: The inverter directs the AC electricity to power the electrical appliances and devices in the premises, enabling you to use the solar-generated electricity directly.
3. Excess Power: If the solar power generated exceeds the immediate power consumption, the excess electricity can be used in two ways:
a. Battery Charging: The hybrid inverter charges the connected batteries with the excess electricity. It converts the excess DC electricity into the appropriate charging current for the batteries.
b. Grid Export: If the batteries are fully charged, the excess AC electricity can be exported back to the electrical grid. In many regions, this allows you to earn credits or receive compensation for the electricity fed back into the grid through net metering or feed-in tariffs.
4. Grid Interaction: If the solar power generation is insufficient to meet the demand, the hybrid inverter automatically draws additional power from the grid to supplement the shortfall.
5. Battery Discharging: When there is a power outage or during periods of high electricity demand, the hybrid inverter can supply power from the batteries. It converts the DC electricity stored in the batteries into AC electricity for use in the premises.
6. Energy Management: The hybrid inverter optimizes energy management by intelligently prioritizing the use of solar power and stored energy. It ensures that the solar electricity is utilized first before drawing power from the batteries or the grid.
7. Monitoring and Control: Hybrid solar inverters often have built-in monitoring and control capabilities. They enable you to monitor the performance of the system, track energy production and consumption, and adjust settings remotely via mobile apps or online platforms.
Overall, a hybrid solar inverter plays a vital role in maximizing the utilization of solar power, managing energy storage, and ensuring a smooth transition between solar, battery, and grid power sources in a solar.