A hybrid solar inverter integrates the capabilities of grid-tied inverters, battery chargers, and off-grid inverters in a single device. It enables seamless operation between solar power, battery storage, and the utility grid, providing greater control, energy independence, and backup power capabilities in a solar system
Brand:
SunArkBrand:
SunArkModel name:
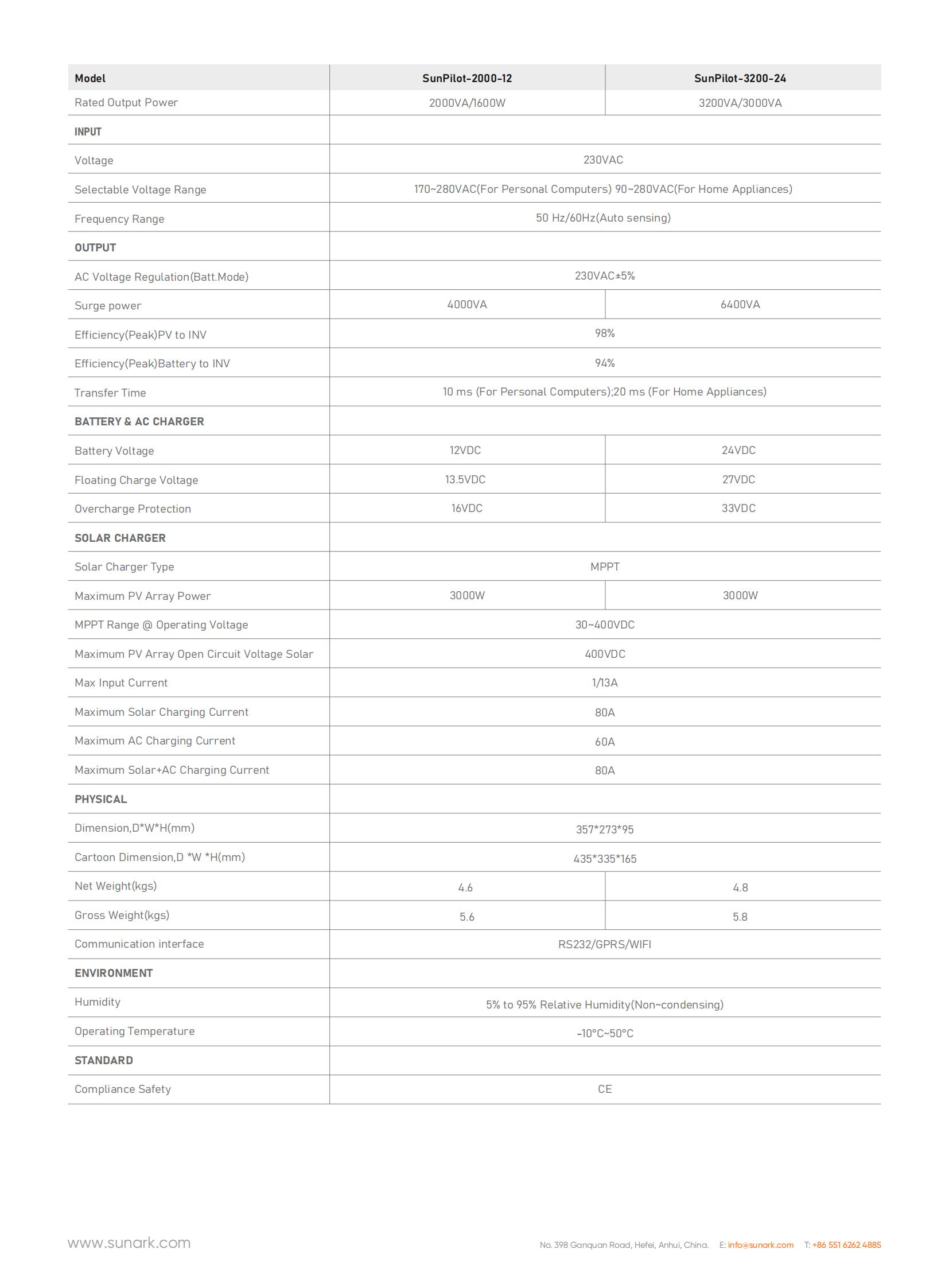
SunPilot-3200-24Max PV power:
3000WMPPT voltage range:
30~400VDCRated output power:
3200VAOutput voltage:
230VAC±5%The datasheet of SunArk SunPilot series 3200VA at below:
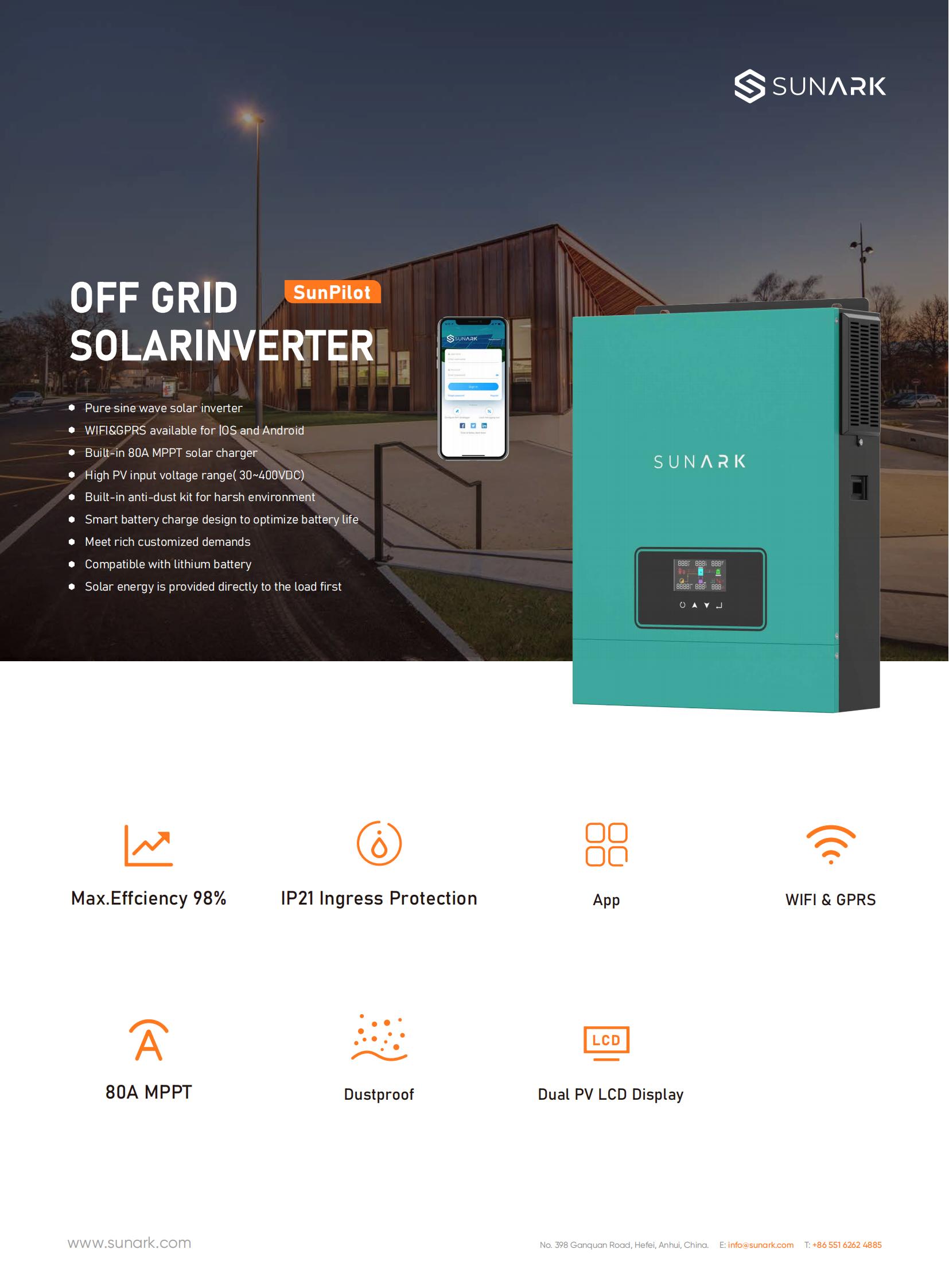
Different colors for option:

A hybrid solar inverter works by managing the flow of electricity in a solar power system, incorporating multiple modes of operation to optimize energy usage. Here is a general explanation of how a hybrid solar inverter works:
Solar Power Mode:
When sunlight falls on the solar panels, they convert the solar energy into DC electricity. The DC electricity is then sent to the hybrid solar inverter.
Grid-Tied Mode:
In grid-tied mode, the hybrid solar inverter synchronizes its output with the utility grid. It converts the DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity, which is compatible with the grid voltage and frequency. The inverter feeds this AC electricity directly into your home or business to power your appliances. Any excess electricity generated is fed back into the grid, and in some cases, credited to your account through net metering schemes.
Battery Charging Mode:
If the hybrid solar inverter is connected to a battery bank, it can utilize the excess solar electricity to charge the batteries. When the solar panels produce more electricity than is being consumed by your home or fed back into the grid, the surplus power is diverted to charge the batteries. The inverter controls the charging process to efficiently fill the batteries to their recommended capacity.
Off-Grid Mode:
If there is a grid outage or you intentionally disconnect from the grid, the hybrid solar inverter can operate in an off-grid mode. In this mode, it draws DC electricity from the solar panels and converts it into AC electricity to power your appliances independently of the utility grid. The inverter uses the energy stored in the batteries to meet the electrical demand during periods when there is insufficient solar power available. The battery bank acts as a backup power supply, providing electricity during cloudy days or at night.
Hybrid Mode:
In hybrid mode, the hybrid solar inverter combines energy from both the solar panels and the utility grid. It intelligently manages the flow of electricity, prioritizing solar power utilization over grid power to minimize grid dependency and reduce energy costs. The inverter constantly monitors the solar generation, battery state of charge, and grid conditions to optimize system performance and maximize self-consumption.
Energy Management:
Hybrid solar inverters often have advanced energy management features. They can implement load shifting, which means scheduling the operation of specific appliances to take advantage of available solar power. For example, the inverter can automatically power high-consumption appliances like washing machines or water heaters during peak solar production times. This helps to reduce reliance on the grid and maximize self-consumption.

The key components and operations of a hybrid inverter in a solar system are as follows:
Solar panel connection: The hybrid inverter is connected to the solar panels on your roof or at a suitable location to capture sunlight. The solar panels convert sunlight into DC (Direct Current) electricity.
MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking): The hybrid inverter typically includes a Maximum Power Point Tracker, which optimizes the electricity output from the solar panels by adjusting the voltage and current to maximize power production.
Grid interaction: The hybrid inverter allows you to feed the excess electricity generated by the solar panels back into the grid. This process is known as "grid-tied" or "net metering." When your solar panels produce more electricity than you are consuming, the excess power is sent back to the grid, and you receive credits or compensation from the utility company.
Battery connection: Hybrid inverters have the capability to connect to a battery bank or energy storage system. During times when your solar panels are not generating enough electricity to meet your demand, the hybrid inverter can draw power from the batteries to supplement the shortfall.
Battery charging: When the solar panels produce more electricity than immediate demand, the excess power can be used to charge the batteries. The hybrid inverter manages the charging process to ensure the batteries are charged efficiently and not overcharged.
Backup power supply: In the event of a power outage or when the grid is not available, a hybrid inverter with batteries can automatically switch to "off-grid" mode, supplying power from the battery bank to essential loads in your home or business. This feature provides backup power during emergencies.
Monitoring and control: Hybrid inverters often come with monitoring and control capabilities. You can monitor the performance, energy production, battery status, and other parameters remotely using monitoring software or mobile applications. Some hybrid inverters also allow you to control charging and discharging of batteries or customize operation settings.
It's important to note that the specific features and functions of a hybrid inverter can vary between different manufacturers and models. When considering a hybrid inverter for your solar system, it's recommended to consult with a professional installer to ensure compatibility and optimal system design