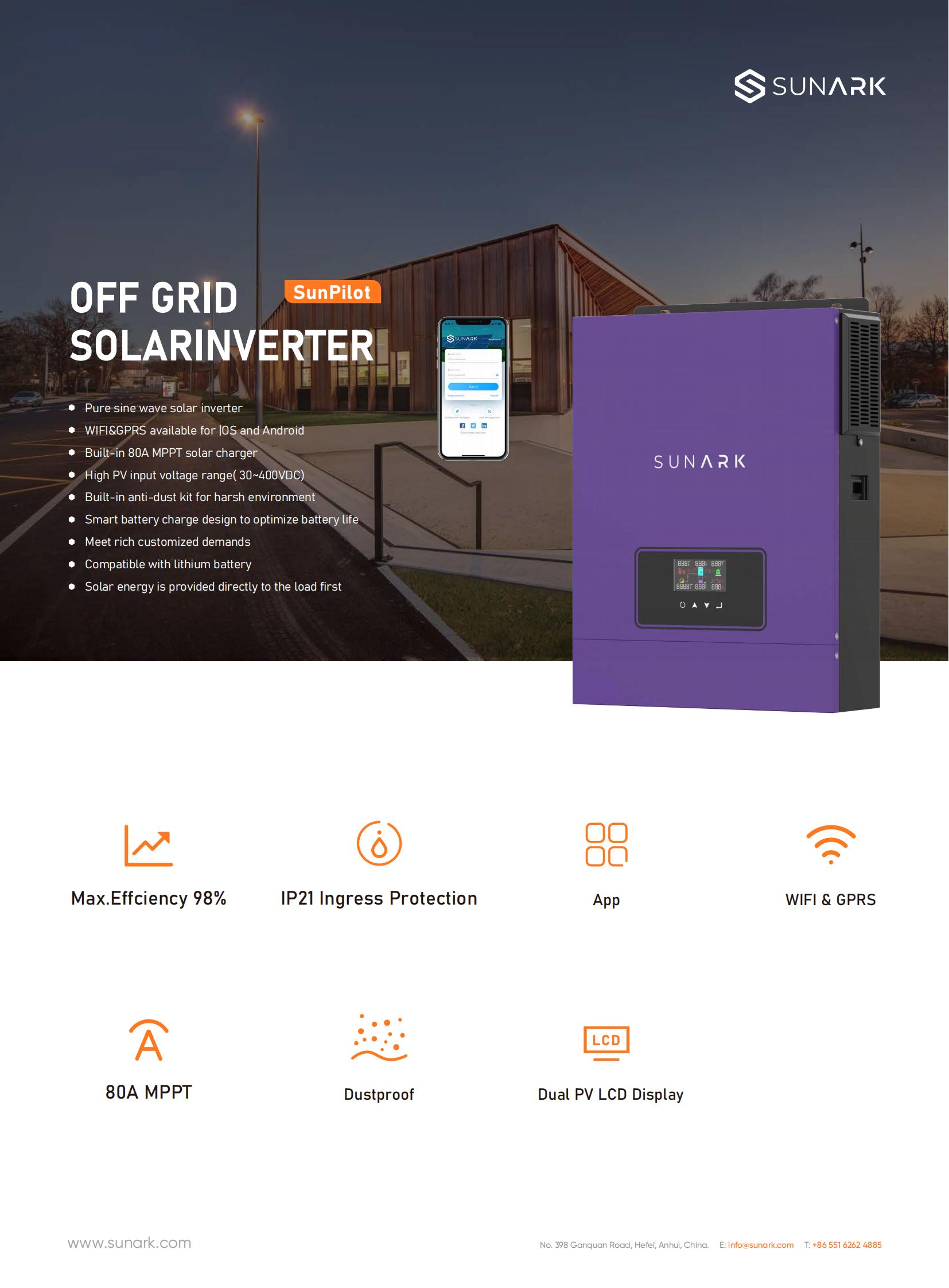
Hybrid solar inverters provide greater flexibility and control over your solar power system, allowing you to maximize self-consumption, increase energy independence, and enhance resilience during power disruptions. They are commonly used in residential and commercial applications where a combination of solar power, grid power, and battery storage is desired.
Brand:
SunArkBrand:
SunArkModel name:
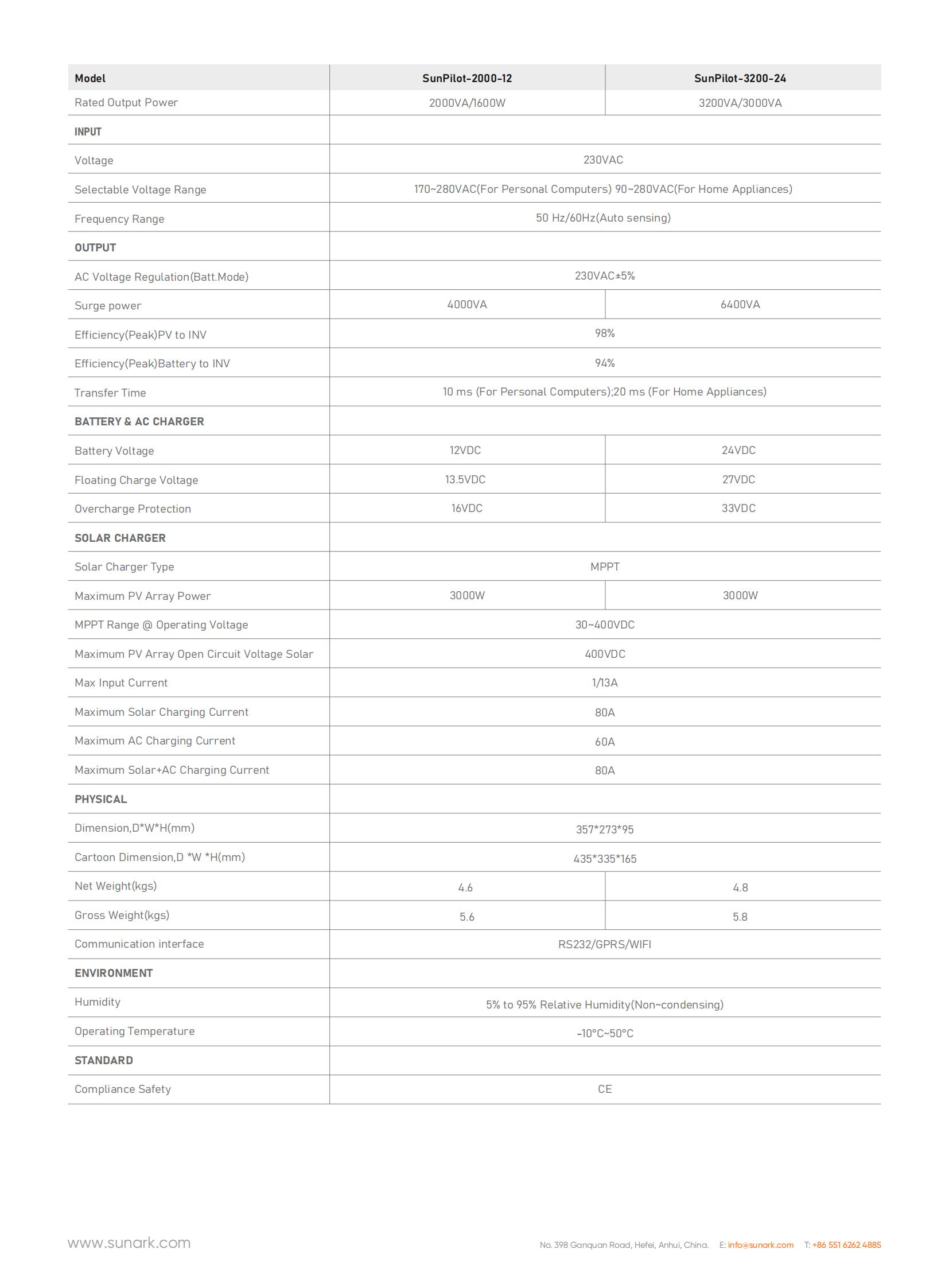
SunPilot-3200-24Max PV power:
3000WMPPT voltage range:
30~400VDCRated output power:
3200VAOutput voltage:
230VAC±5%The datasheet of SunArk SunPilot series 3200VA at below:
Different colors for option:

What sets a hybrid solar inverter apart from a regular solar inverter is its ability to operate in multiple modes. It can function as a grid-tied inverter when the utility power is available, as an off-grid inverter when there is no utility power, and as a hybrid inverter when both solar power and utility power are present. This versatility allows the inverter to maximize energy usage and provide backup power during blackouts.
Some key features of a hybrid solar inverter include:
Grid-tie functionality: During the daytime, when the solar panels generate more electricity than is being consumed, the excess power can be fed back into the grid, reducing your dependence on utility power and potentially earning you credits or incentives through net metering programs.
Battery storage compatibility: Hybrid solar inverters can be connected to batteries, which enable the storage of excess solar energy for later use, such as during the night or during power outages. The inverter manages the charging and discharging of the batteries, ensuring efficient utilization of stored energy.
Backup power supply: In the event of a grid outage, hybrid solar inverters can activate their backup power supply function, using the stored energy in the batteries to power essential loads in your home or business until the grid power is restored.
Energy management: Hybrid inverters often come with advanced energy management features, such as load shifting and peak shaving. Load shifting allows you to schedule the usage of appliances to coincide with when solar power is available, optimizing self-consumption and reducing reliance on the grid. Peak shaving helps reduce peak demand charges by limiting the amount of power drawn from the grid during peak load periods.

In a solar system, a hybrid inverter works by managing the flow of electricity between various components, such as solar panels, batteries, and the electrical grid. Here is a general overview of how a hybrid inverter operates:
Solar panel operation: The solar panels generate DC electricity from sunlight. This DC electricity is then directed to the hybrid inverter.
Grid-tie mode: If the electrical grid is available and utility power is stable, the hybrid inverter can work in grid-tie mode. In this mode, the inverter converts the DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity that can be used to power household appliances. Any excess electricity produced by the solar panels can be fed back into the grid, reducing your reliance on utility power. The inverter synchronizes the produced AC power with the grid voltage and frequency to ensure compatibility.
Battery charging: If a battery storage system is installed, the hybrid inverter can charge the batteries with the excess solar power during the daytime. The inverter manages the charging process, regulating the voltage and current to ensure efficient battery charging. It monitors the battery state-of-charge and adjusts the charging rate accordingly.
Backup power supply: During grid outages or when the hybrid inverter detects a loss of utility power, it can automatically switch to backup power mode. The inverter utilizes the energy stored in the batteries to supply AC power for essential loads in your home or business. The backup power supply provides electricity until the grid power is restored.
Grid support and energy management: Some hybrid inverters have additional features for grid support and energy management. For example, they can support grid stabilization by injecting reactive power into the grid or dynamically control the power flow between the solar panels, batteries, and the grid. Energy management functionalities allow the inverter to optimize energy usage, such as prioritizing self-consumption, managing battery discharge, and load shifting.
Monitoring and control: Hybrid inverters often come with monitoring and control systems that allow users to monitor the performance of the solar system, track energy production and consumption, and adjust various operating parameters. Some inverters can be connected to online platforms or mobile apps for remote monitoring and control.
Overall, a hybrid inverter acts as the central control unit in a solar system, managing the flow of electricity between solar panels, batteries, and the grid. It maximizes the utilization of solar power, provides backup power during outages, and offers advanced energy management capabilities to optimize energy and cost savings.